LinSSID
LinSSID fills the gap of a graphical WLAN scanner, after the InSSider is apparently no longer developed for Linux. The development of LinSSID is also stalling; the last update found on the Sourceforge project page dates back to 2018. However, since then some necessary updates including a manual were published ny the Debian project which went downstream to Ubuntu.
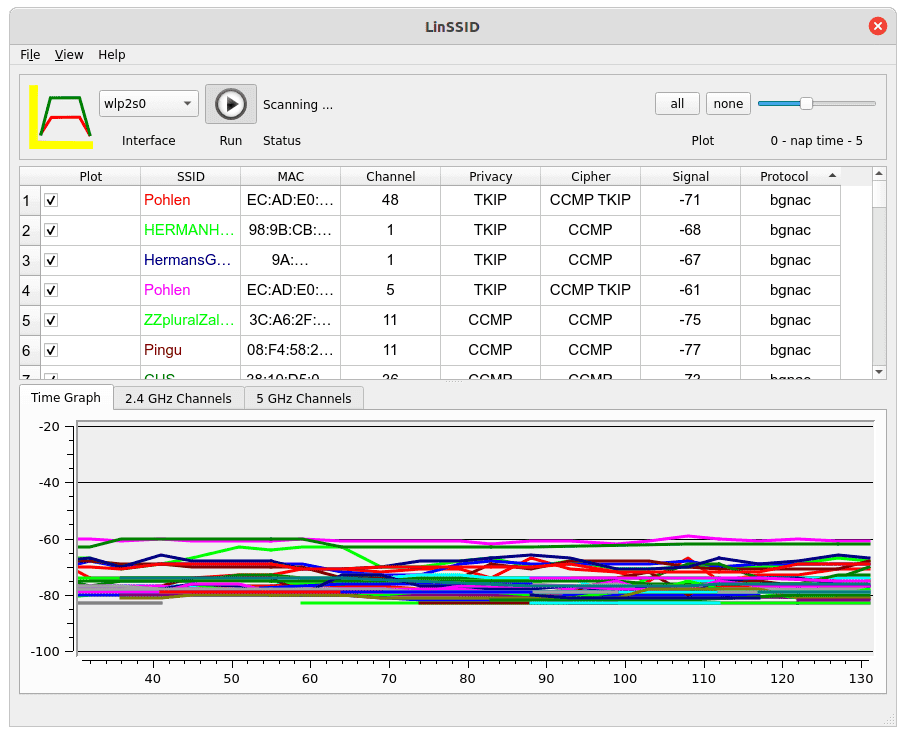
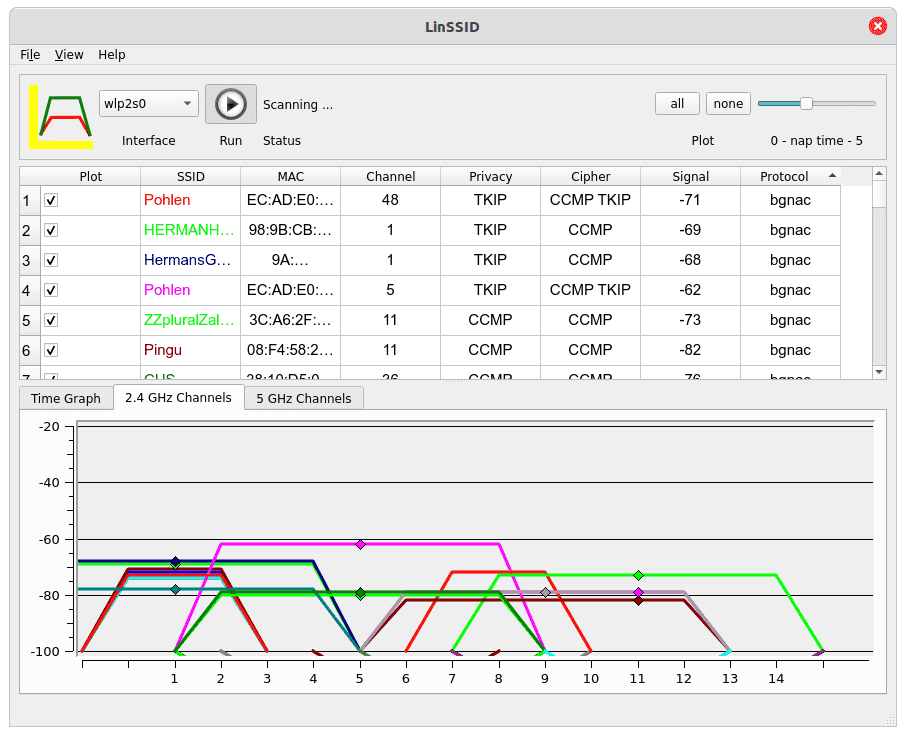
So the program can still be installed in its latest version from Ubuntu’s Universe repository and does what it should do, provided that the own user account belongs to the group of administrators: With a click on Start, LinSSID scans the location in the 2.4 and (if available) 5 MHz band and prepares the result graphically: either on a time axis or as a diagram with channel/signal strength.
Installation
sudo apt install linssid
Alternatives
There is a huge number of network and security tools for Linux, which are of course able to scan wifi networks. Typical network tools installed on every Ubuntu system are Network-Manager und iwlist, replaced by iw.
Here is an example to list all available wireless networks (including information on channel, rate, signal strength and encryption) using nmcli, the command line interface of Network-Manager:
nmcli device wifi
